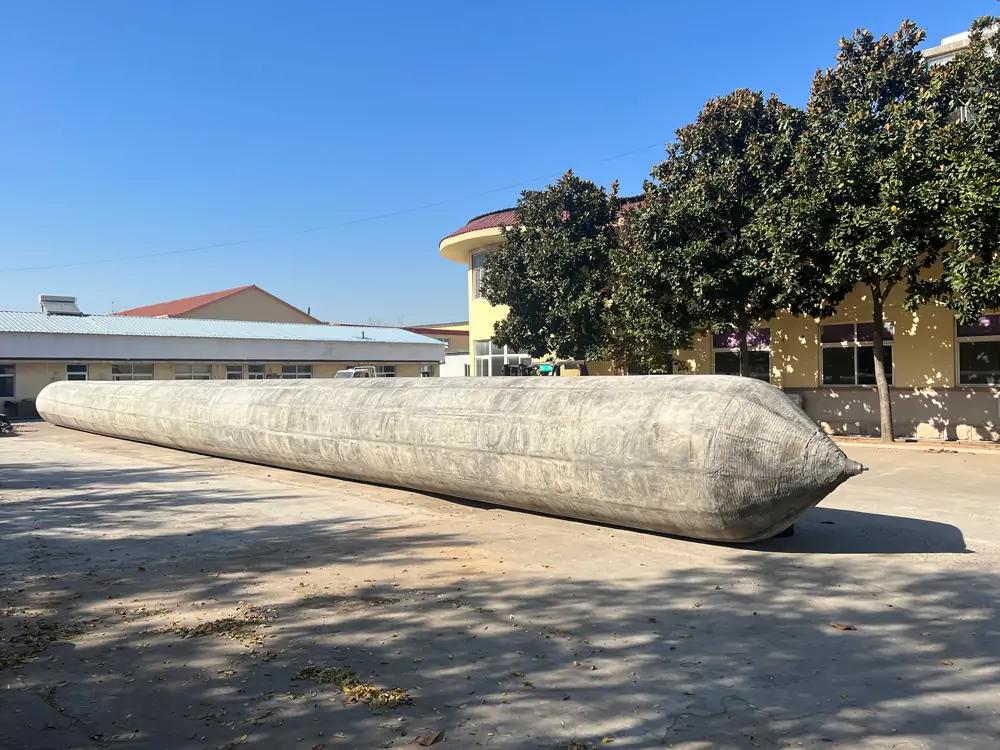
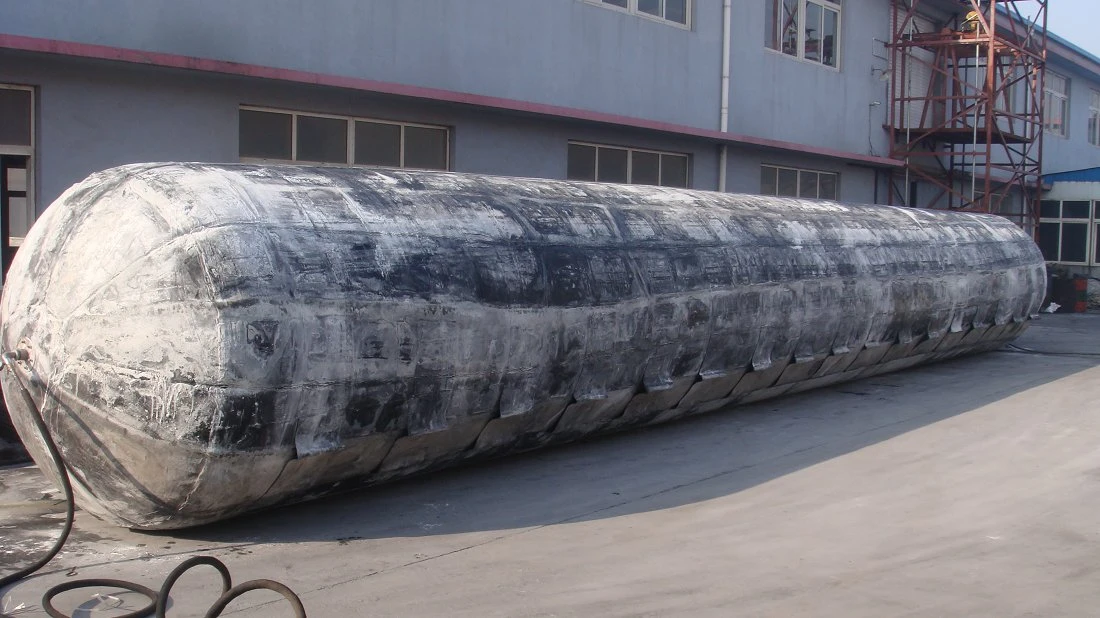
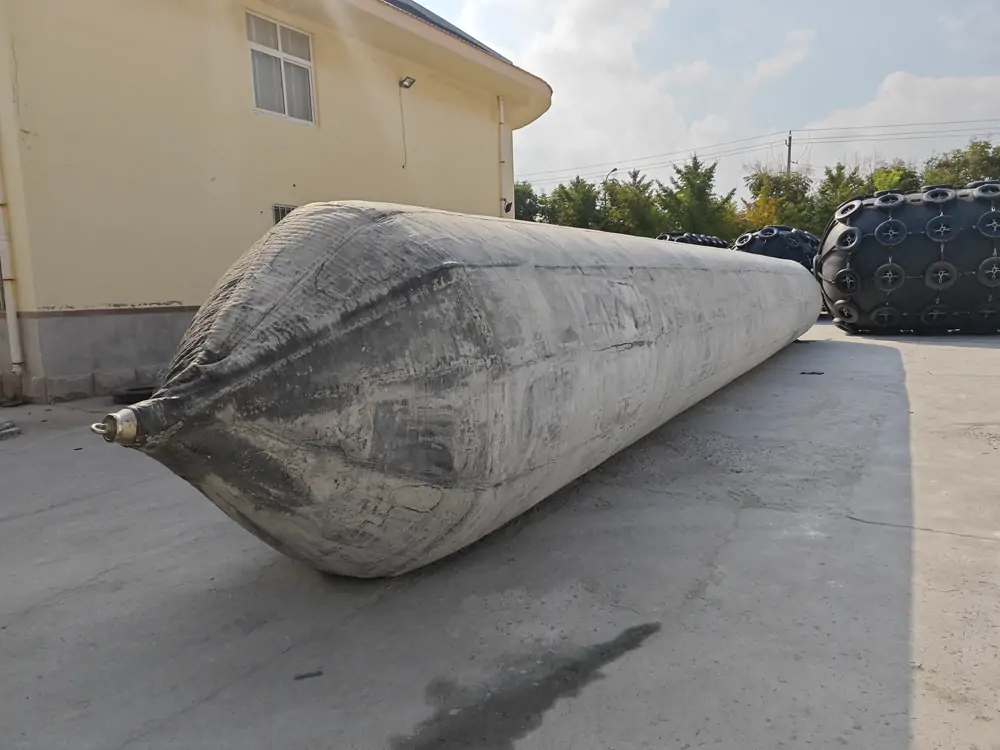
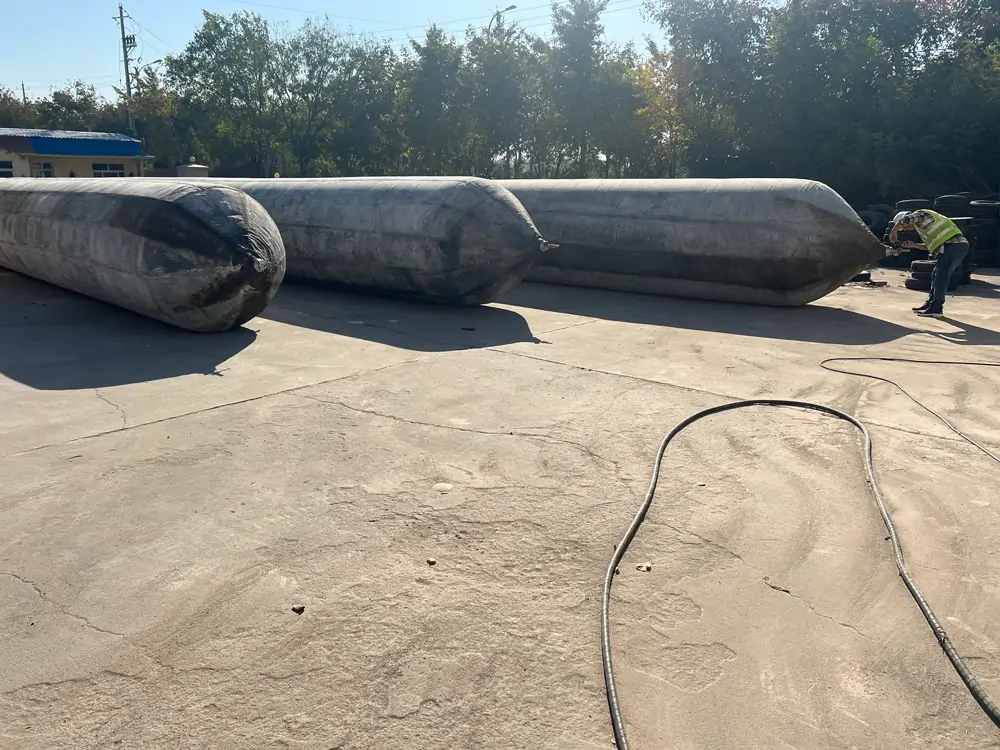
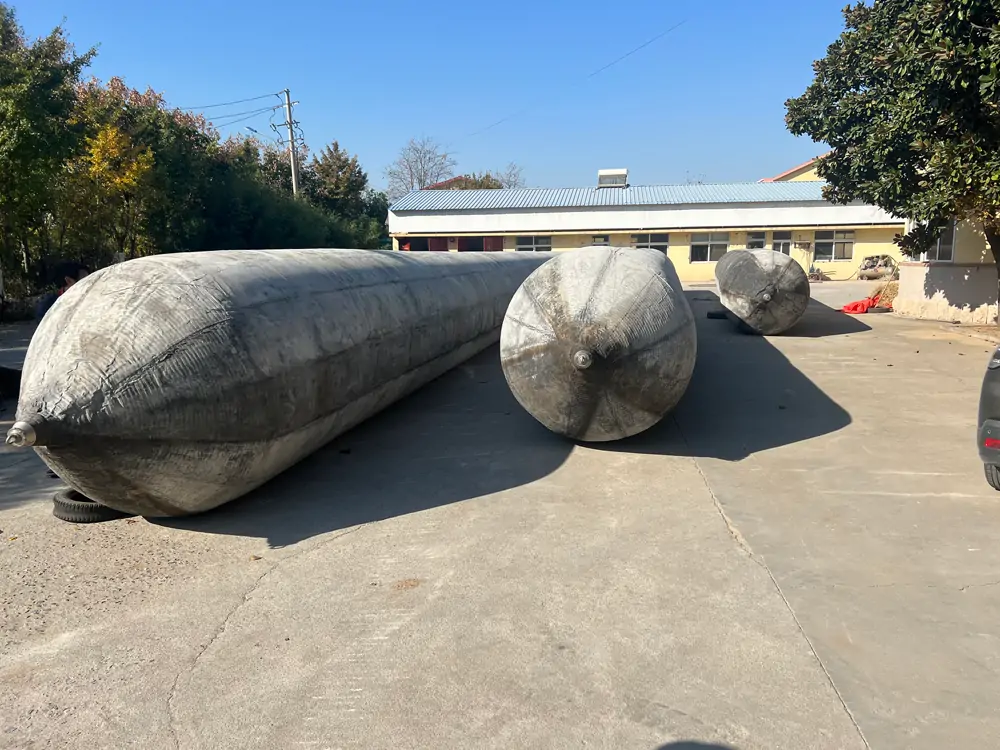
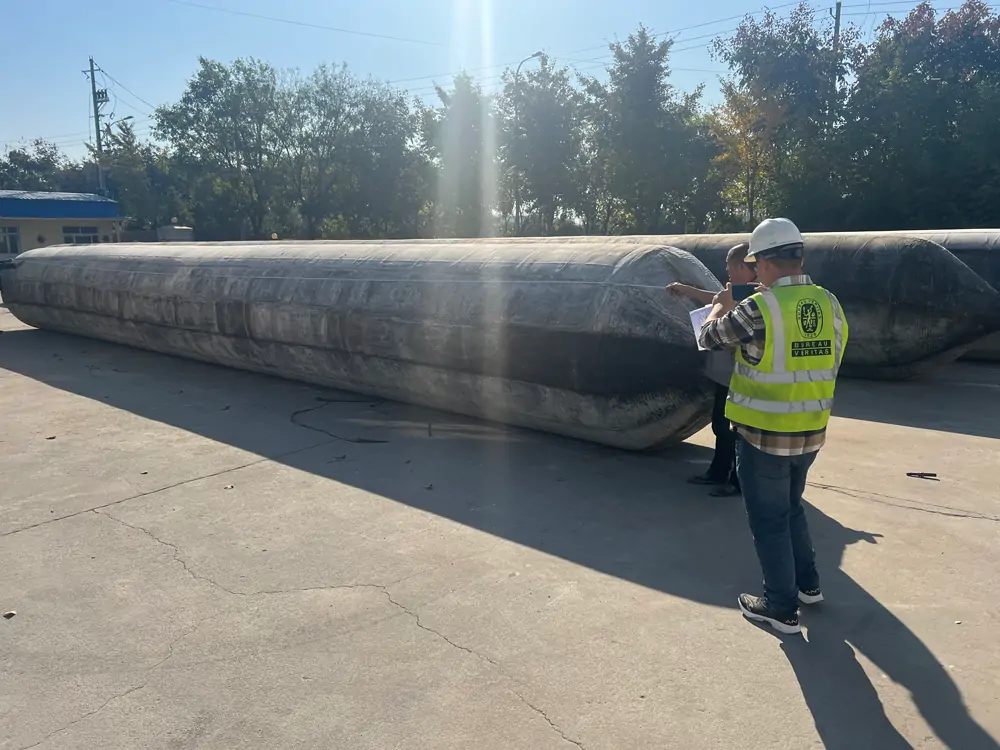
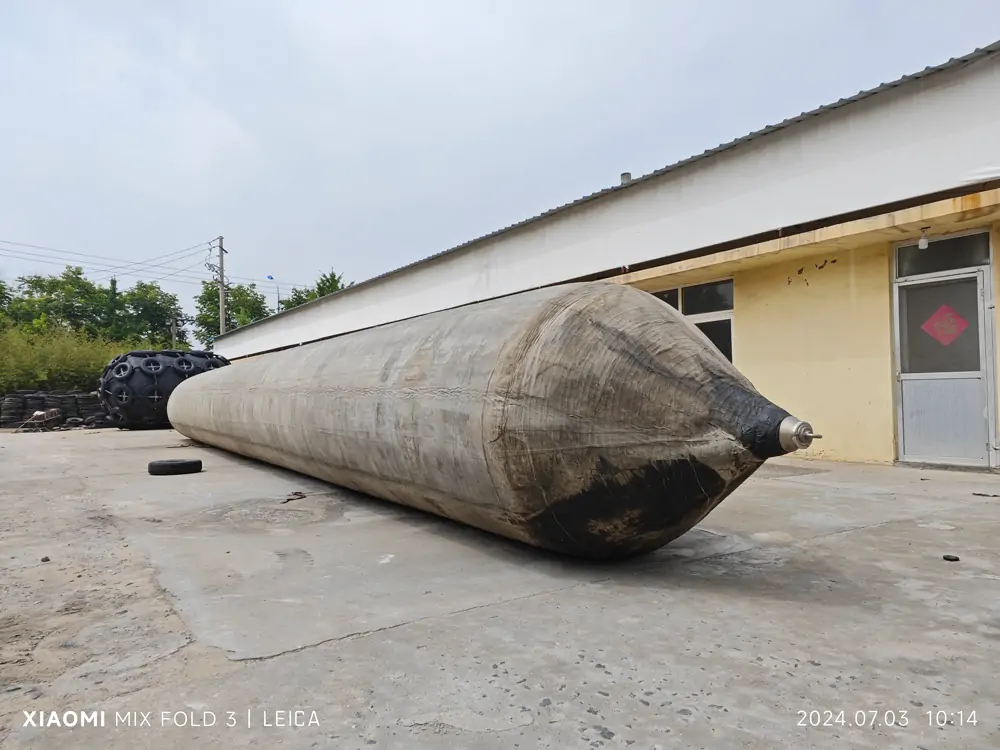
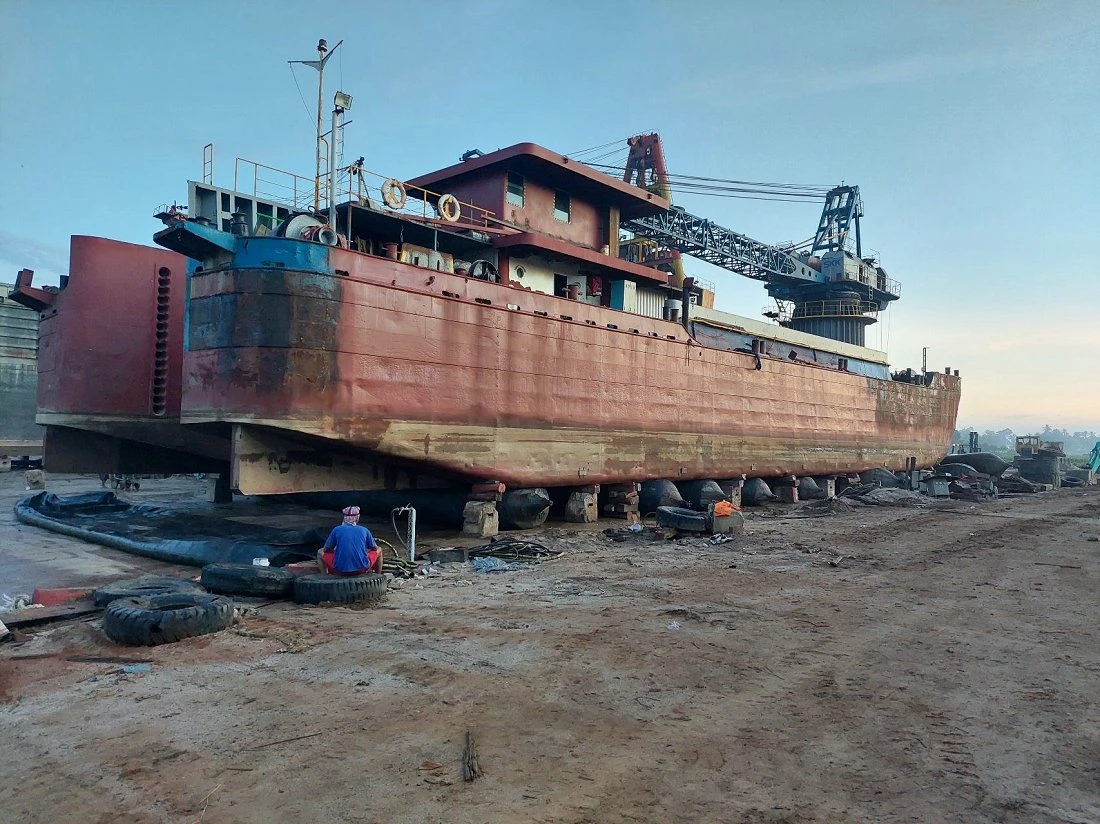
Jerryborg Marine Ship Launching Airbags
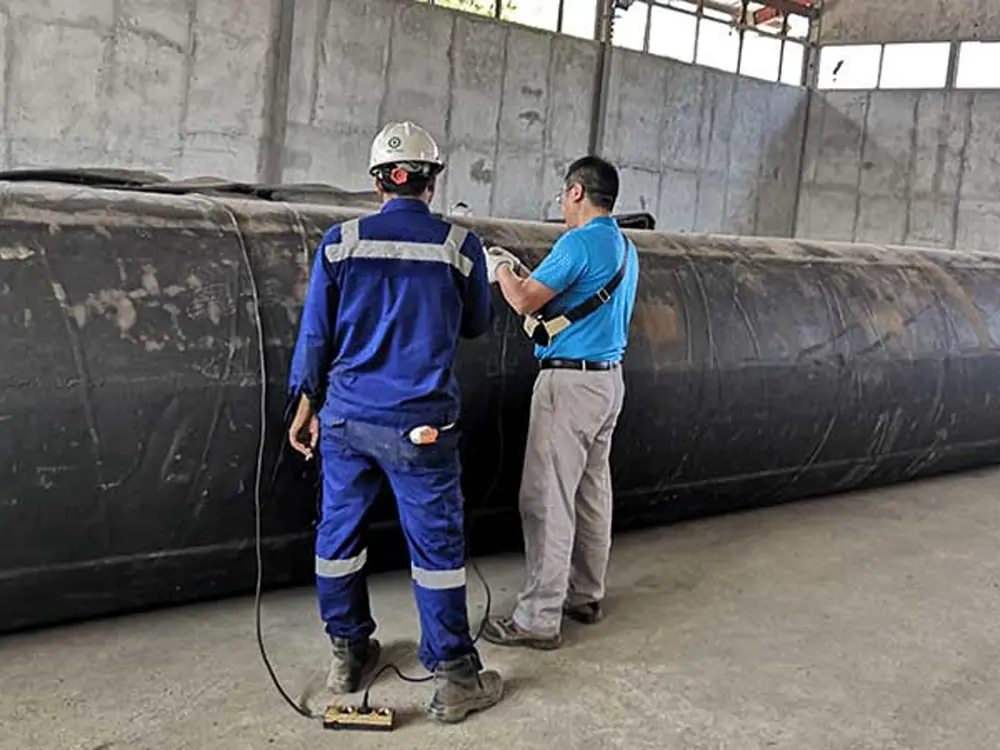
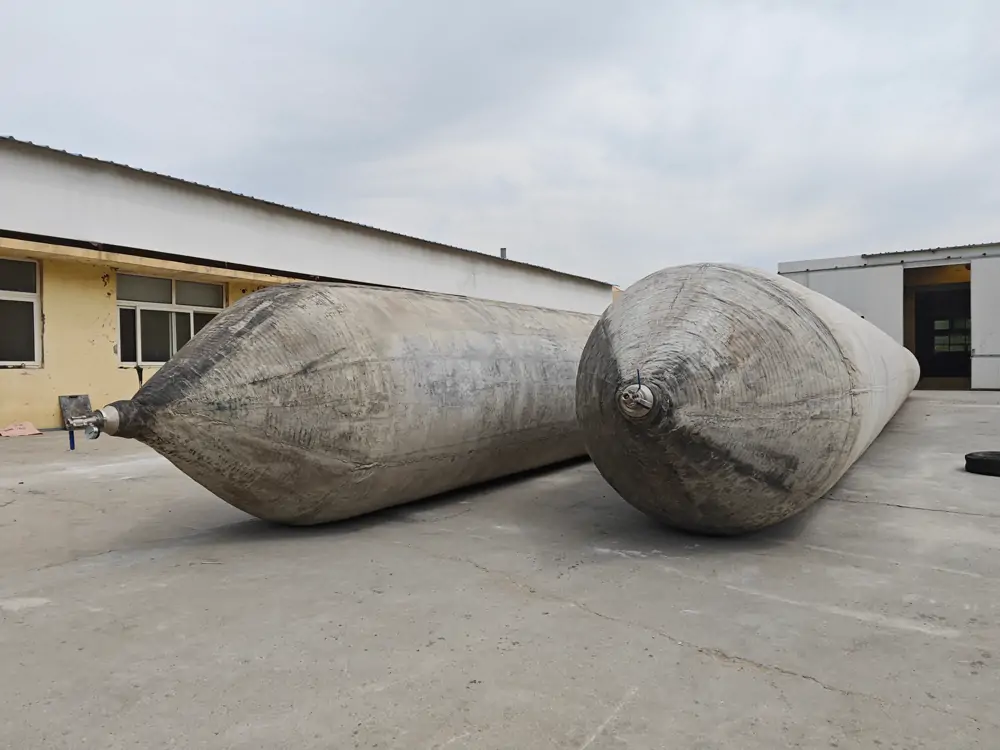
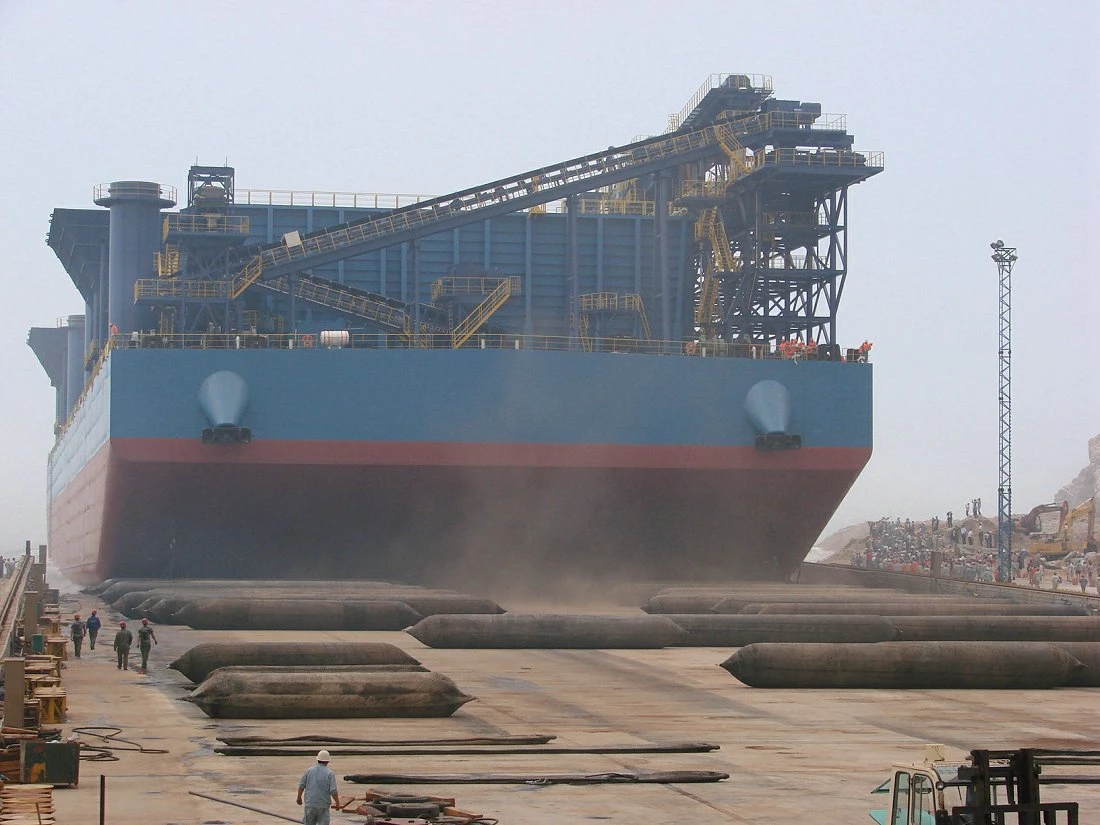
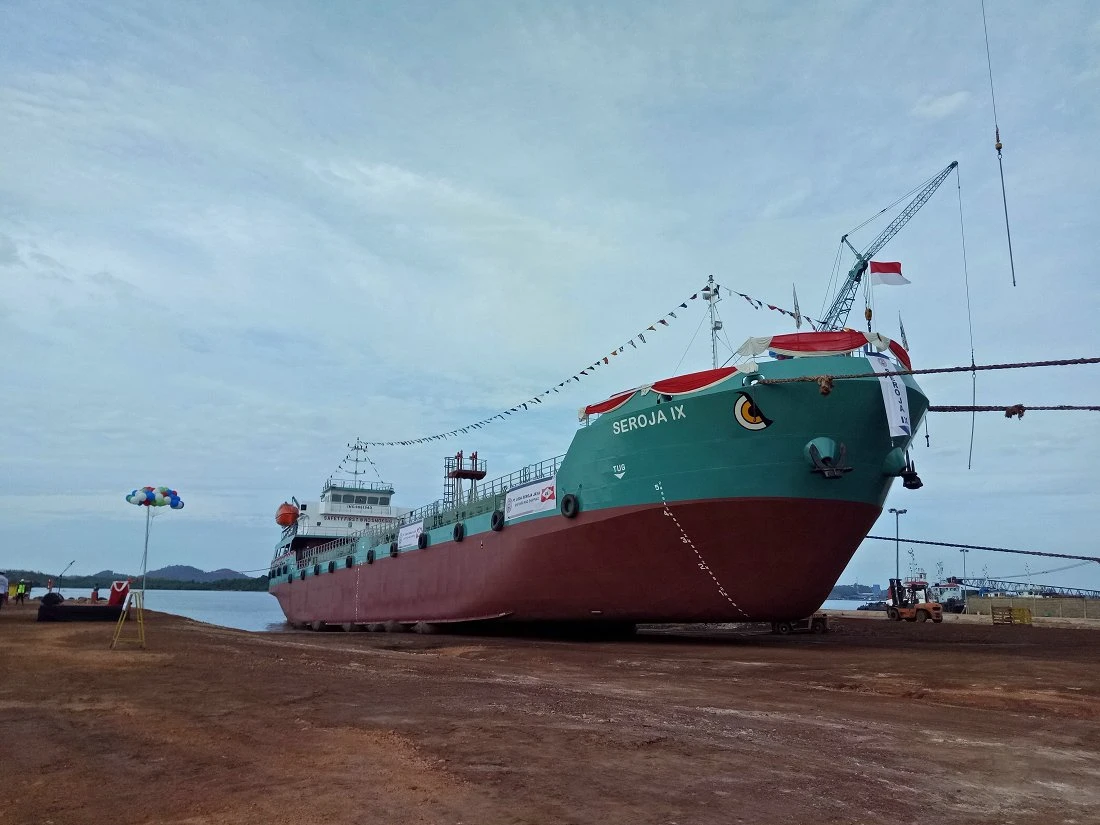
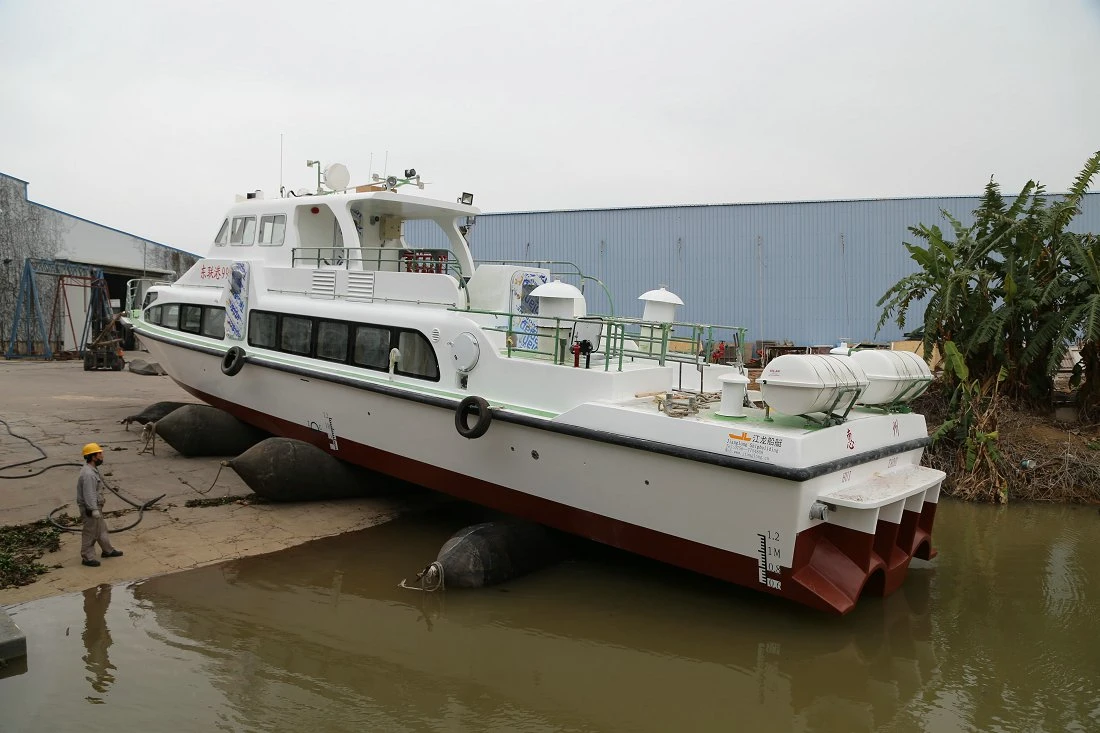
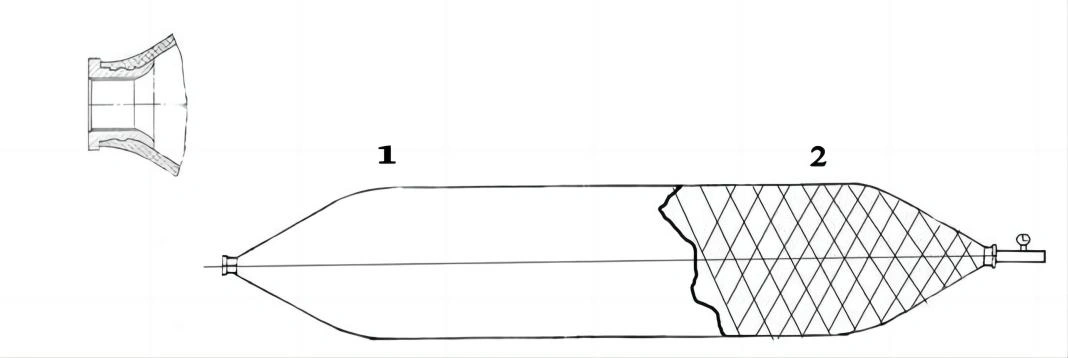
Marine launching airbags are also known as marine upslip airbags, ship downslip balloons, inflatable marine airbags, or boat lifting airbags. These airbags have a special rubber construction. It overcomes the limits of traditional water launch methods. The flexible ship-launching method is an emerging and promising technology in the field of shipbuilding and ship repair. This technology solves the limits of traditional fixed rail launches. It also improves the productivity of small and medium-sized shipyards. Due to its time-saving, economical, flexible, and safe features, it has been widely used by shipyards around the world.
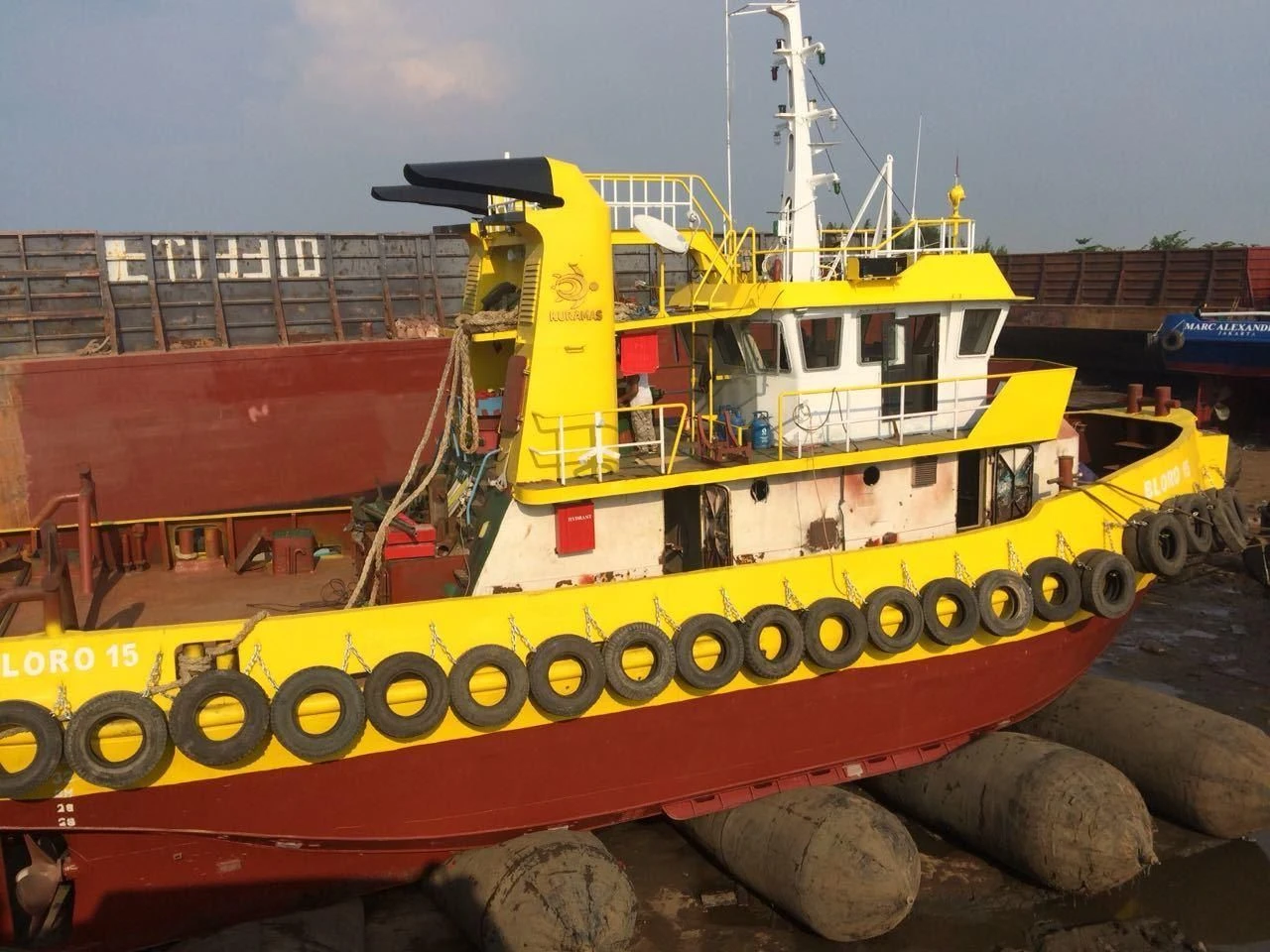
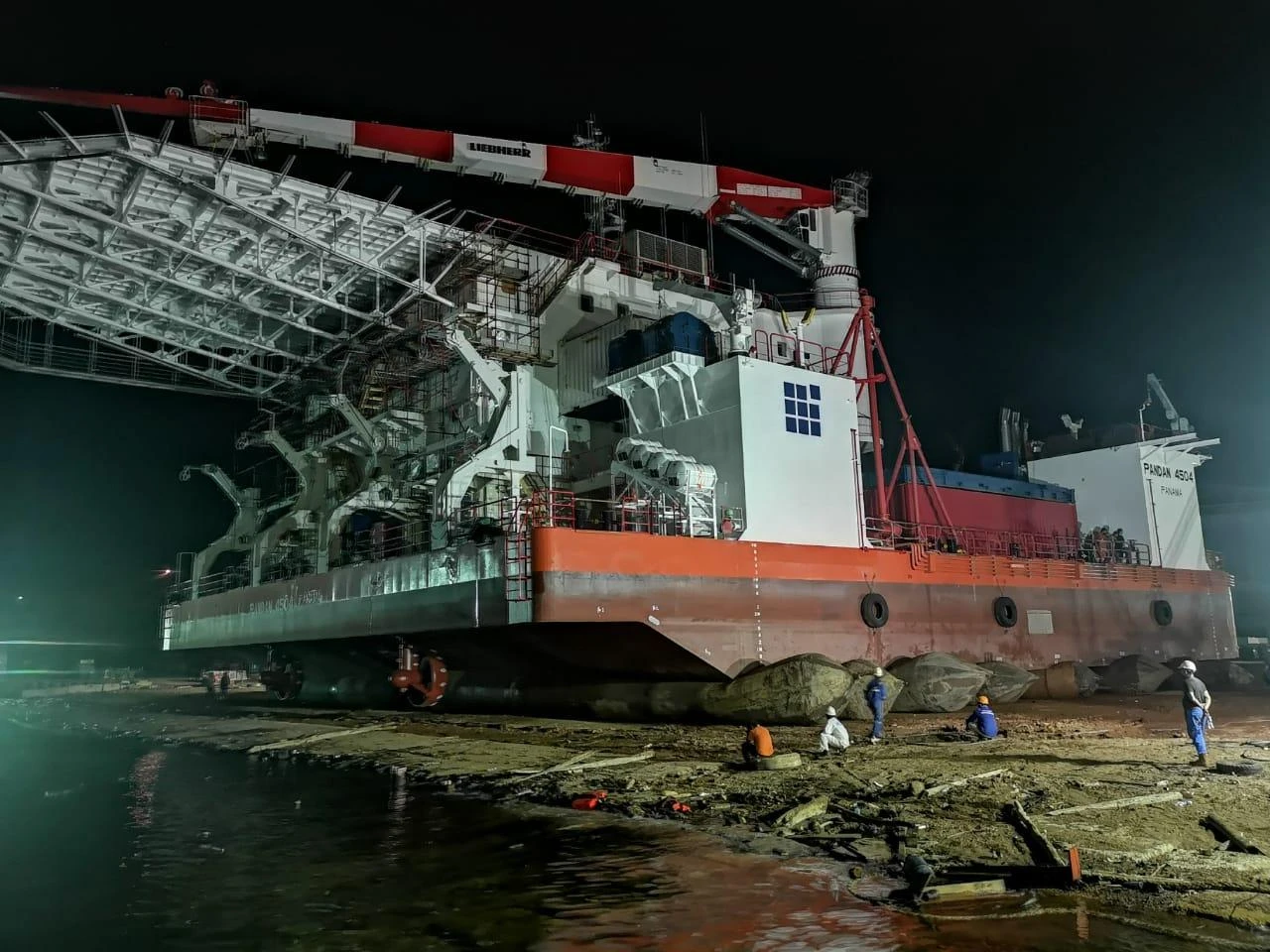
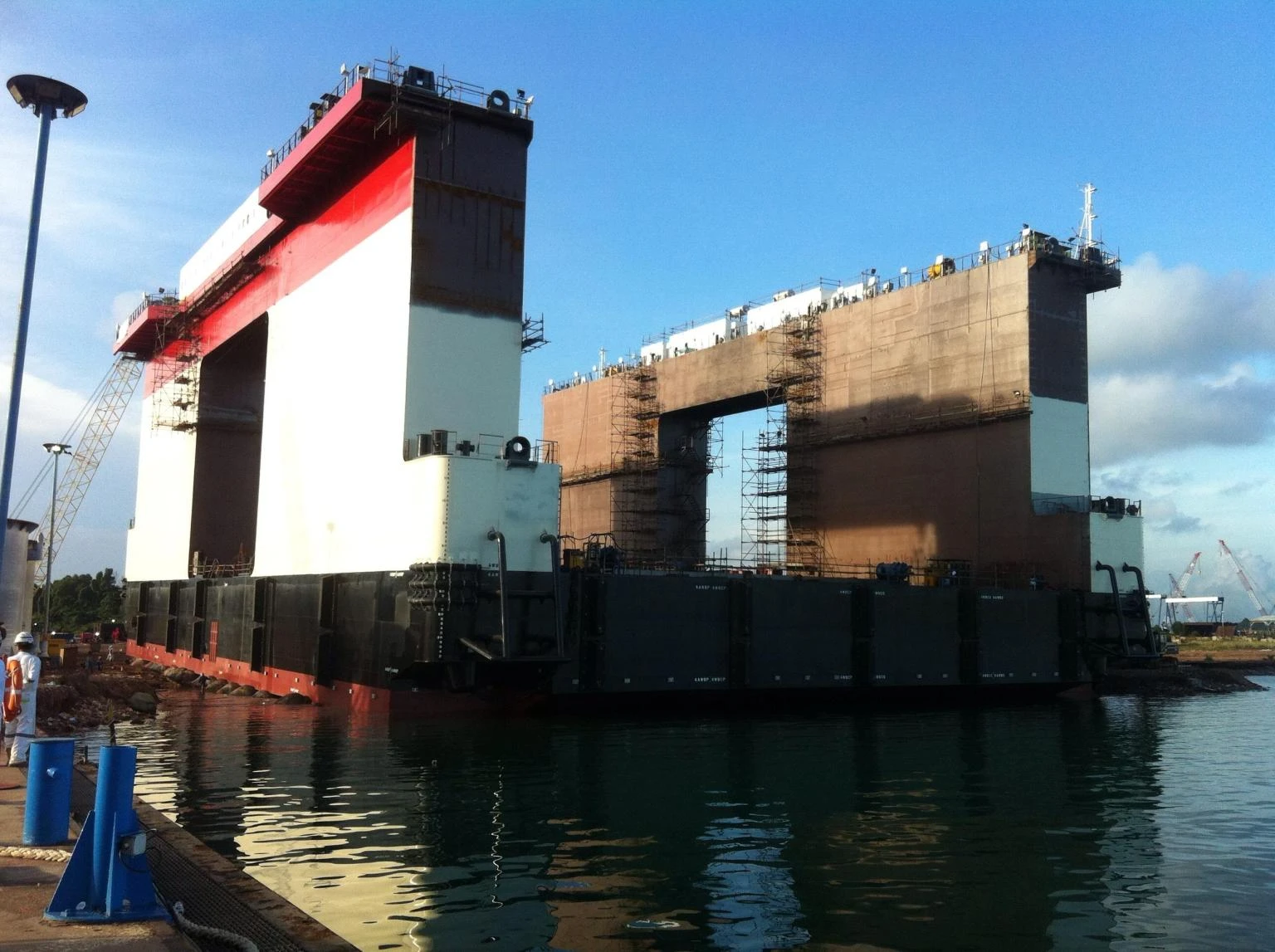
These marine airbags are widely used for the launching and landing of cargo ships, the lifting of sunken ships, and the rescue of stranded ships. Flexible launch technology provides significant versatility. Rubber airbags help the shipbuilding and maritime industries. They reduce workload, save time, and cut effort and investment needs.
Jerryborg Marine is a leading manufacturer of rubber airbags/marine inflatable airbags compliant with ISO14409:2011 or CB/T 3795 standards. We provide ship launching, repair, and mobilization services to shipyards and trading companies on six continents. Our ship-launching bladders come in diameters up to 2.5m and lengths up to 26m. They can support and carry structures weighing over 10,000 tonnes. Some of our marine airbags can reach diameters of up to 4.0m for salvage buoyancy.